Share
Pin
Tweet
Send
Share
Send
Also, very often I met such a situation when the manufacturer of various electronics accelerates low-power transistors to the limit, as a result, they heat up a bit. This tactic is not reliable, and sooner or later a weak link will be felt.
To avoid this and get out of a difficult situation, I will show how to make a radiator for small transistors.
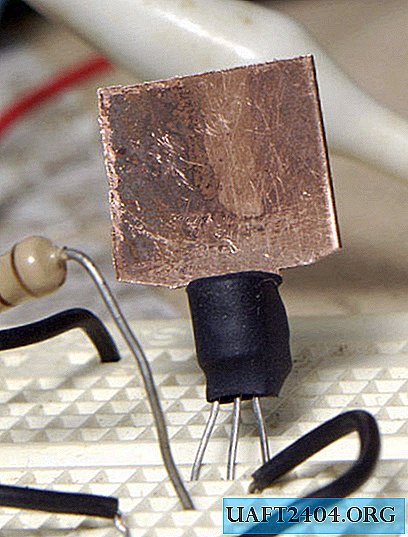

To do this, cut out a radiator from a piece of tin, and preferably aluminum.


This is how it all looks.

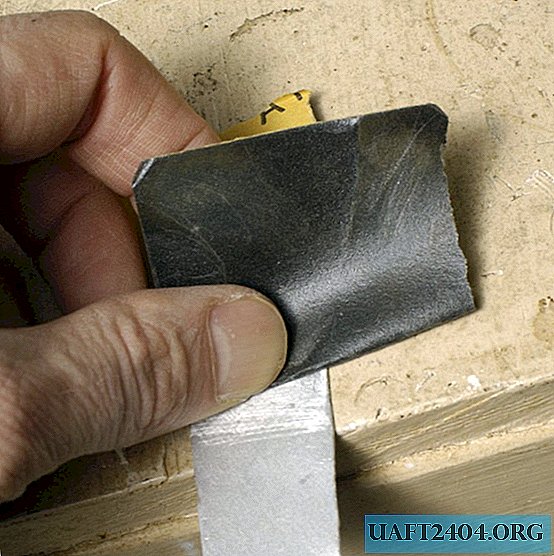
In the presence of sharp edges we clean with sandpaper.

We also need a heat-conducting paste and a piece of heat shrink tube.

So, the assembly. We smear the transistor with the paste, the side that will be adjacent to the radiator.

We put the tube on the radiator and insert the transistor.

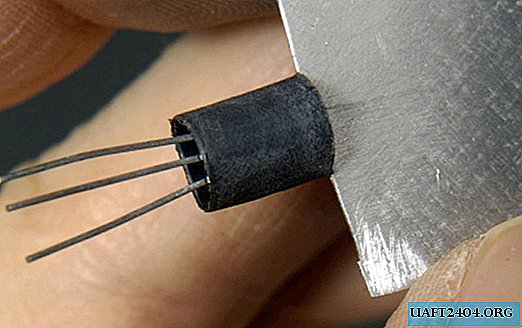
Blow the heat shrink with a hairdryer.
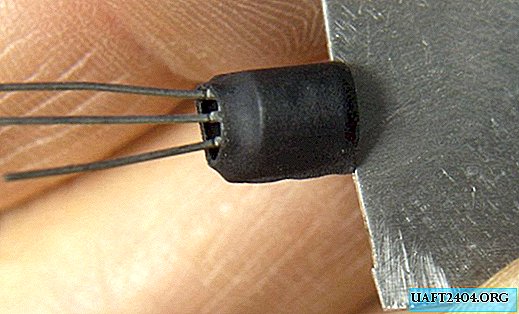
The radiator is ready. It can be bent.

As a result of such a simple refinement, the power of the transistor almost doubled from 0.5-0.8 W to 1.2-1.8 W.
To prove excellent work, I put a transistor with a radiator under a power of 2.75 watts. It worked without problems, with little heating, for 3 hours and did not burn out.
Of course, this method will help you out, but if you have the opportunity to put more powerful transistors that are designed to fit on a radiator, then choose them.
Share
Pin
Tweet
Send
Share
Send











